Key Points
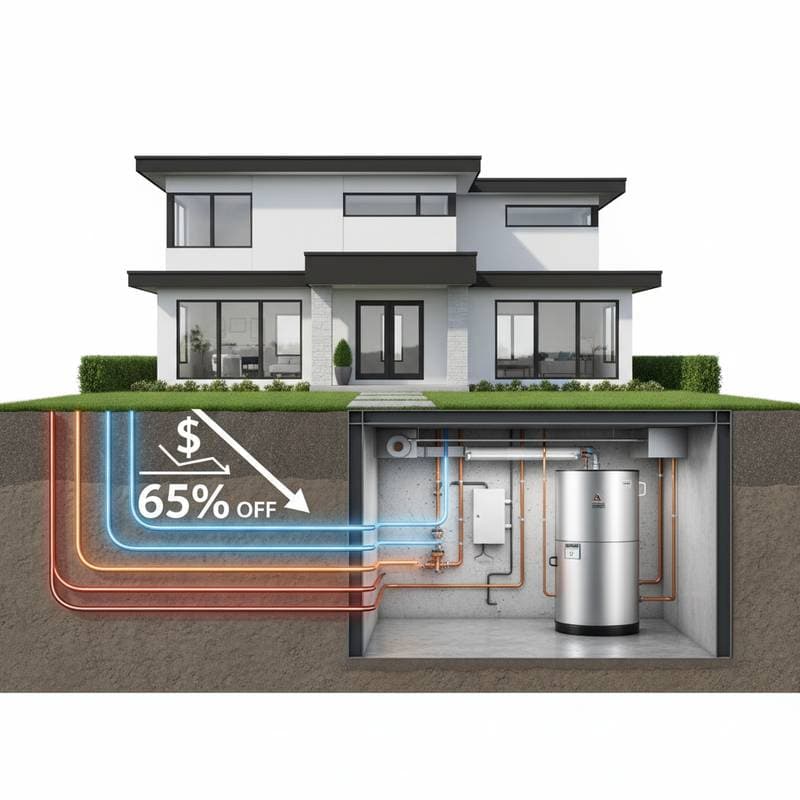
- Geothermal heat pumps reduce heating and cooling costs by up to 65 percent compared to traditional HVAC systems.
- These systems leverage the earth's consistent underground temperature as a renewable energy source.
- Initial installation expenses exceed those of conventional systems, yet energy savings and incentives typically recover costs within six to ten years.
- Configurations include horizontal, vertical, and pond loops, selected based on property size and soil type.
- Optimal performance demands precise design, accurate sizing, and installation by certified professionals.
Harnessing Earth's Steady Energy
Picture a heating and cooling setup that operates silently, pulling warmth from the soil under your property rather than consuming fuel or drawing heavily from the power grid. Without the hum of an outdoor unit or the ups and downs of energy bills, this approach delivers reliable comfort year-round. Geothermal heat pumps, also known as ground-source systems, make this possible.
Homeowners often wonder about the financial benefits. Properly engineered and installed, these systems lower HVAC expenses by approximately two-thirds. To grasp the full picture, consider the mechanics, expenses, and tailored calculations for your residence.
Financial and Environmental Advantages
Conventional heating and cooling depend on variable resources such as natural gas or electricity, which affect both costs and performance. Geothermal systems draw on the earth's unchanging temperature just below the surface, serving as a natural thermal storage. During winter, the pump extracts heat from the ground and transfers it indoors. In summer, it removes excess heat from the home and deposits it into the earth.
This process boosts efficiency significantly. For each unit of electricity powering the pump, the system provides three to five units of heating or cooling. Such performance cuts utility bills substantially and minimizes environmental impact through reduced emissions.
Geothermal setups enhance indoor conditions as well. They sustain even temperatures and humidity, eliminating drafts and preventing overly dry air.
Assessing Suitability for Your Property
Evaluate key factors before proceeding with installation to confirm compatibility.
Site Evaluation
- Land area and soil type: Horizontal loops need ample space but involve lower installation costs. Vertical loops suit compact lots, though they require deeper drilling.
- Water resources: Open-loop designs utilize groundwater, subject to local quality standards and permits.
Home Efficiency Assessment
- Insulation levels and sealing: A well-insulated structure allows for a more compact system, lowering initial outlay.
- Current duct infrastructure: Aging ducts might necessitate repairs or adjustments to accommodate the system's requirements.
Professional Selection
Select an installer with geothermal expertise. Professionals conduct thermal conductivity tests and precise load assessments to maximize system effectiveness.
Investment Analysis and Payback
Initial prices may seem daunting, yet sustained savings shift the equation. Residential installations generally cost between 15,000 and 35,000 dollars, influenced by capacity, terrain, and loop type.
Breakdown of Upfront Expenses
- Horizontal closed loop: 15,000 to 25,000 dollars.
- Vertical closed loop: 20,000 to 35,000 dollars.
- Pond or lake loop: 12,000 to 25,000 dollars, provided water access exists.
In contrast, efficient air-source alternatives range from 8,000 to 15,000 dollars. Geothermal options reduce yearly energy use by 50 to 65 percent, yielding payback in six to ten years, contingent on rates and rebates.
Consider a family with 2,400 dollars in annual heating and cooling costs. Savings could reach 1,300 to 1,500 dollars each year. Across 20 years, this accumulates to substantial gains, plus potential rises in home equity.
Enduring Benefits
- Longevity: Ground loops endure 50 years or longer, while indoor units last 20 to 25 years, surpassing standard HVAC durability.
- Maintenance needs: Fewer components mean reduced upkeep expenses.
- Financial aids: Incentives in various areas cut initial costs by 20 to 40 percent.
System Configurations and Integration
Tailor the design to your site for seamless operation.
Closed-Loop Options
- Horizontal loops: Pipes laid in trenches four to six feet underground, best for expansive, soft-soil properties.
- Vertical loops: Drilled shafts extending 100 to 400 feet, appropriate for constrained or rocky areas.
- Pond or lake loops: Submerged coils in adjacent water, providing superior heat exchange where feasible.
Open-Loop Designs
These systems pump groundwater through the exchanger and return it to the earth or a separate well. Efficiency is high, but water purity and regulations apply.
Within the home, connect the unit to existing ducts or underfloor heating. Certain models also supply hot water, enhancing overall utility.
Performance Variables
Multiple elements shape costs and outcomes.
- Soil heat transfer properties: Sandy versus clay or rocky ground influences pipe length and excavation depth.
- Regional weather: Harsh winters might call for extended loops or auxiliary support.
- Utility pricing: Elevated electricity rates accelerate returns.
- Contractor proficiency: Accurate sizing and layout ensure peak operation.
Obtain a comprehensive load analysis and savings projection prior to approval.
Enhancing with Complementary Upgrades
Integrate geothermal with other improvements for amplified results.
Strategic Pairings
- Solar panels: Counterbalance pump electricity for minimal running costs.
- Advanced windows and insulation: Diminish energy needs, enabling downsized systems and quicker recovery.
- Room-specific controls: Customize settings for optimal use and comfort.
- Eco-friendly finishes: Select materials that support the system's humidity regulation for healthier interiors.
Environmentally, these systems avoid fossil fuel burning, curbing emissions and elevating air quality both indoors and out.
Common Questions Addressed
Installation timeline? Residential projects span one to two weeks, varying with ground conditions and weather.
Viability in cold areas? Affirmative. Stable ground temperatures enable heat extraction even in subzero conditions.
Backup requirements? Rare, though extreme climates may benefit from minor supplemental heating for peak demands.
Upkeep routine? Annual inspections suffice, including filter replacements and loop checks.
Impact on property value? Yes, efficiency-focused buyers value the lower costs and green attributes, often boosting appraisals.
Retrofitting feasibility? Possible, involving site work and duct modifications; many legacy homes transition successfully from fossil fuels.
Funding options? Low-rate loans through banks and energy initiatives ease upfront burdens while capturing savings.
Steps to Implementation
Approach geothermal adoption methodically for optimal results. Start with an energy audit to benchmark your home's efficiency. Solicit proposals from accredited installers, verify credentials, and analyze cost forecasts.
Realizing Sustained Comfort and Savings
Geothermal integration fortifies your home against rising energy demands. Expect consistent temperatures, reduced bills, and a lighter ecological footprint. This upgrade positions your property for enduring value and resilience.